A Step-by-Step Whiteboard Exercise to Visualise Information Flows and Identify Delays
In today’s fast-paced world, organisations are striving to enhance efficiency and productivity. While much of the focus has been on streamlining physical processes, it’s crucial not to overlook knowledge work—the intellectual activities that involve generating, sharing, and applying information. For teams engaged in knowledge work, understanding and optimising workflows can lead to significant improvements. One powerful tool for achieving this is Value Stream Mapping (VSM).
What is Value Stream Mapping?
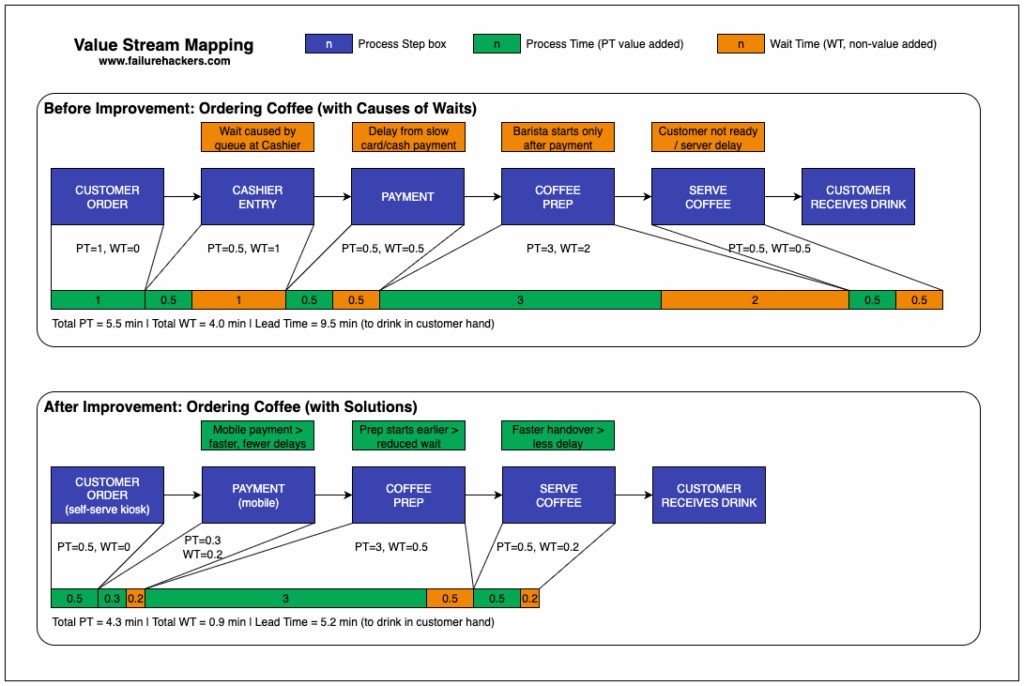
Value Stream Mapping is a lean management technique used to visualise the flow of materials and information required to bring a product or service to the customer. In the context of knowledge work, it helps teams understand how information flows through an organisation, highlighting areas where delays or inefficiencies occur.
Why Use VSM for Knowledge Work?
- Clarifies processes: By mapping out workflows, teams can see the entire picture, including hand-offs between team members and departments.
- Identifies waste: VSM helps to pinpoint areas of waste—activities that do not add value to the end product or service.
- Encourages collaboration: The exercise of creating a value stream map fosters open discussion among team members, resulting in shared understanding and commitment to improvement.
- Enhances continuous improvement: VSM aligns with the principles of continuous improvement by providing measurable insights.
Preparing for the Whiteboard Exercise
Before diving into the mapping exercise, it’s essential to prepare adequately. Here’s how you can set the stage:
1. Gather Your Team
Bring together individuals involved in the workflow you wish to analyse. This could include team members from different departments, stakeholders, and anyone who contributes to or relies on the flow of information.
2. Define the Scope
Clearly outline the process you intend to map. It could be a specific project timeline, a product development cycle, or a customer service process. Be precise about where the mapping will begin and end.
3. Set Up Your Whiteboard
You’ll need a large whiteboard or several flip charts. Ensure you have markers in different colours to distinguish elements within your map. You may also want sticky notes, which can help in representing individual tasks or elements flexibly.
Step-by-Step Whiteboard Exercise to Map Information Flows
Let’s break down the exercise into manageable steps.
Step 1: Identify Customer Value
Start by asking, “What does our customer consider valuable?” Write this at the top of the whiteboard to keep the team focused on delivering value. Discuss how your team’s output supports customer needs.
Step 2: List Major Activities
Ask team members to identify the major activities involved in delivering the knowledge work. Typical activities might include research, writing, reviewing, and distribution. Write these down in sequential order along the left side of the whiteboard. Use arrows to indicate the flow from one activity to the next.
Step 3: Map Information Flows
Now, illustrate the flow of information between activities. Use arrows or lines to connect the activities, showing how information is transmitted. For example, after research, information may flow to a writer, who then passes their draft to a reviewer. Label the arrows with the type of information shared (e.g., draft documents, feedback) and any tools used (e.g., email, collaboration software).
Step 4: Identify Hand-Off Points
Look for points where ownership of tasks changes—these are critical hand-off points. Mark these distinctly on the whiteboard. Discuss the implications of each hand-off. Is there a risk of miscommunication? Does information get lost or delayed? Engage the team in identifying potential problems that may arise during these transitions.
Step 5: Assess Delays and Waste
Next, assess each step for potential delays. Use symbols to represent different types of waste according to Lean principles (e.g., overproduction, waiting, defects). As you discuss each step, ask questions like:
- How long does each task take?
- What factors contribute to delays?
- Are there redundant steps that could be eliminated?
Encourage team members to share experiences and insights. Document identified problems next to the relevant activities.
Step 6: Highlight Opportunities for Improvement
Once you’ve assessed the workflow, shift focus to potential improvements. Brainstorm ideas collectively. For instance, could any steps be automated? Can communication be streamlined? Are there tools that would facilitate smoother transitions? Use sticky notes for proposed solutions and place them next to the relevant activities.
Step 7: Create an Action Plan
Conclude the exercise by developing an action plan based on your mapping. Assign team members to specific tasks, define timelines, and establish follow-up meetings to track progress. Document all insights and decisions made during the exercise for future reference.
Post-Exercise Reflection
After the session, take time to reflect on what you’ve learned. Encourage team members to share feedback on the exercise itself—what worked well, what could be improved, and how they felt about the discussions. This reflection will help refine the approach for future VSM exercises.
Practical Application
To apply the knowledge gained from your VSM exercise, consider implementing the following actions:
- Keep the Map Visible: Display the value stream map in your workspace as a constant reminder of the identified processes and areas for improvement.
- Regular Reviews: Schedule regular review sessions (e.g., monthly or quarterly) to revisit the map, assess changes, and identify new areas for optimisation.
- Document Changes: Track changes made as a result of the exercise and measure their impact. Collect data on time saved, reduction in errors, or improved communication to demonstrate the value of the exercise.
- Cultivate a Continuous Improvement Culture: Encourage team members to regularly identify and propose improvements, fostering an environment that values innovation and efficiency.
Conclusion
Value Stream Mapping is a powerful tool for analysing and optimising workflows in knowledge work. By visually representing information flows, hand-offs, and delays, teams can collaboratively pinpoint inefficiencies and develop actionable solutions. Engaging in this whiteboard exercise not only enhances understanding but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement. So gather your team, set up your whiteboard, and start mapping the value stream today—your customers (and your team) will thank you for it!